Concurrent Hash Table Designs: Synchronized, Sharding, ConcurrentHashMap, and NonBlockingHashMap
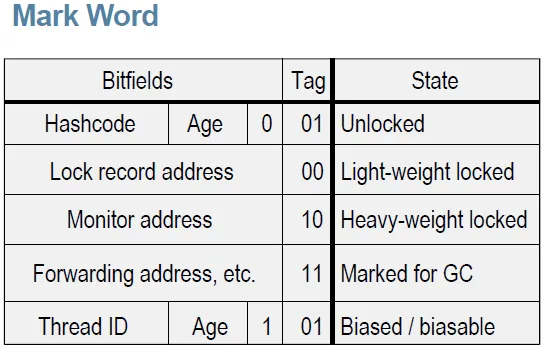
Discussions Hacker News Reddit The next milestone is to build a fully thread-safe hash map. Up to this point, the focus has been entirely on single-threaded performance: minimizing memory overhead, improving cache locality, and squeezing out every last bit of throughput from the underlying data layout. However, real-world applications rarely stay single-threaded. To be practically useful, a hash map must behave correctly—and efficiently—under concurrent access. Before jumping straight into implementation, it’s worth stepping back and studying how existing thread-safe hash map implementations approach this problem. Different designs make different trade-offs between simplicity, scalability, memory usage, and read/write performance. By examining these approaches side by side, we can better understand which ideas scale cleanly—and where the pitfalls are—when multiple threads hit the same structure at once. ...