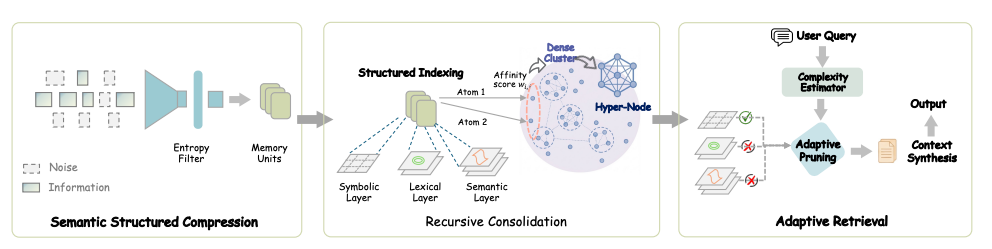
[논문 리뷰] SimpleMem: Efficient Lifelong Memory for LLM Agents
이 글은 SimpleMem: Efficient Lifelong Memory for LLM Agents을 읽고 리뷰한 글입니다. 현재는 논문의 일부 내용이 수정되어 작성 시점(2026.01.24)과 상이할 수 있습니다. 배경 LLM은 기본적으로 상태가 없는(stateless)한 특징을 갖고 있습니다. 따라서, 이전 추론 결과가 다음 추론 결과에 영향을 주지 않습니다. 이러한 특성으로 인해, LLM을 그냥 사용하면 대화가 연속적으로 이어지지 못 하는 문제가 발생할 수 있습니다. 즉, 나와 방금 나눈 대화를 기억하지 못 하는 초단기 기억 상실증 같은 모습을 보이는 것입니다. 연구자들은 간단한 방법으로 이 문제를 해결하였습니다. 바로 사용자와 LLM 에이전트 사이의 대화 이력을 별도의 공간(e.g. 메모리)에 저장하고, 매 추론마다 입력 프롬프트에 과거 대화 이력을 주입함으로써 LLM으로 하여금 연속적인 대화가 가능하도록 만든 것입니다. ...
Concurrent Hash Table Designs: Synchronized, Sharding, ConcurrentHashMap, and NonBlockingHashMap EN
Discussions Hacker News Reddit The next milestone is to build a fully thread-safe hash map. Up to this point, the focus has been entirely on single-threaded performance: minimizing memory overhead, improving cache locality, and squeezing out every last bit of throughput from the underlying data layout. However, real-world applications rarely stay single-threaded. To be practically useful, a hash map must behave correctly—and efficiently—under concurrent access. Before jumping straight into implementation, it’s worth stepping back and studying how existing thread-safe hash map implementations approach this problem. Different designs make different trade-offs between simplicity, scalability, memory usage, and read/write performance. By examining these approaches side by side, we can better understand which ideas scale cleanly—and where the pitfalls are—when multiple threads hit the same structure at once. ...
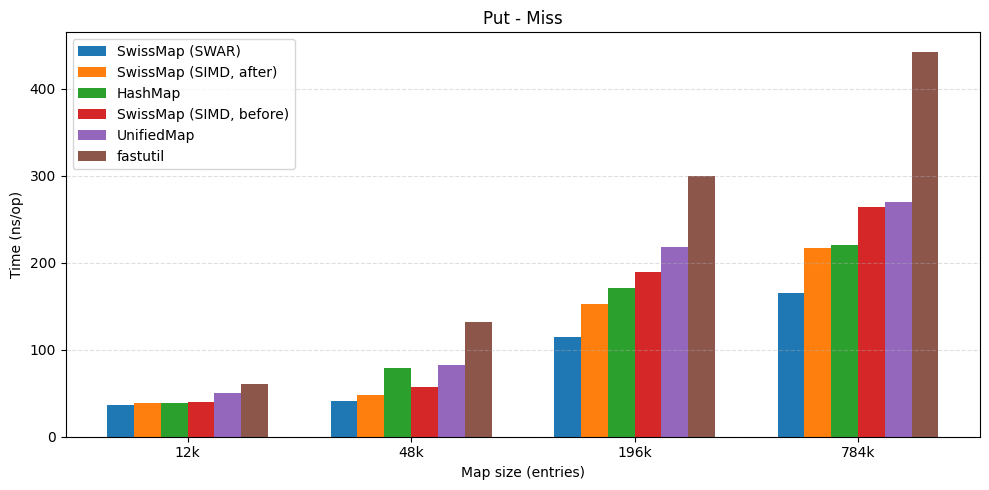
Further Optimizing my Java SwissTable: Profile Pollution and SWAR Probing EN
Discussions Reddit Part 2: optimizing the hot path (and finding a weird villain) “Why Objects.equals() showed up in the profile—and why SWAR beat the Vector API on ARM (and x86). In the last post, I finally got a SwissTable-ish map running on the JVM and fast enough to make me smile. Naturally, that meant I immediately started staring at the profiler again, thinking: okay… but how do I make it faster? ...
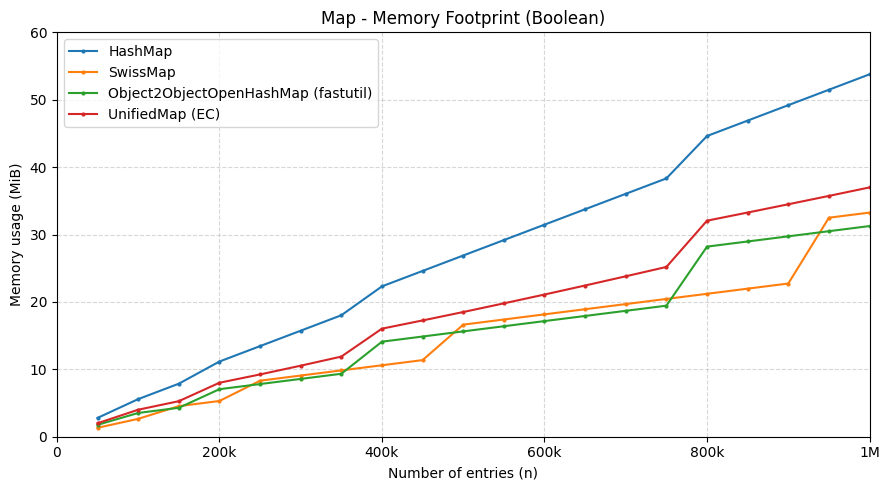
Building a Fast, Memory-Efficient Hash Table in Java (by borrowing the best ideas) EN
Discussions Hacker News Reddit One day, I ran into SwissTable—the kind of design that makes you squint, grin, and immediately regret every naive linear-probing table you’ve ever shipped. This post is the story of how I tried to bring that same “why is this so fast?” feeling into Java. It’s part deep dive, part engineering diary, and part cautionary tale about performance work. 1) The SwissTable project, explained the way it feels when you first understand it SwissTable is an open-addressing hash table design that came out of Google’s work and was famously presented as a new C++ hash table approach (and later shipped in Abseil). ...
Inside Google’s Swiss Table: A High-Performance Hash Table Explained EN
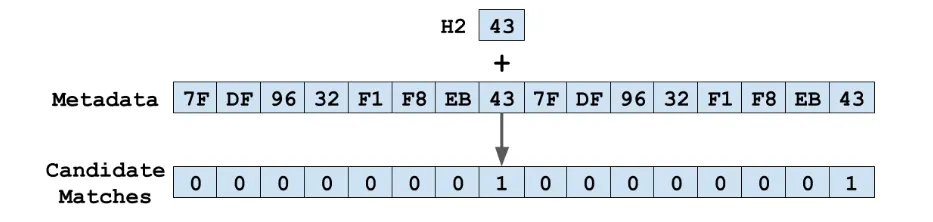
Swiss Tables:A Modern, High-Performance Hash Table Swiss Table is a high-performance hash table design introduced by Google engineers in 2017. It has since inspired many standard-library implementations across languages, including: Go 1.24 ships its map with this design (up to 60% faster) Rust’s standard HashMap has also moved from Robin Hood hashing to a Swiss Table-inspired layout. Datadog reported as much as 70% memory savings after migrating to Swiss Table Open Addressing, Briefly An open addressing hash table is one of the implementation methods for hash tables. Unlike separate chaining — which uses external data structures such as linked lists or trees — open addressing implements the entire hash table as a single contiguous array. ...
SIMD JSON: Unlocking Maximum Performance for JSON Deserialization EN
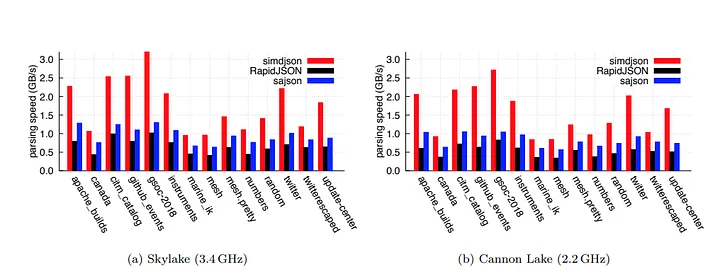
Limitations of Traditional Scalar State Machine Parsers The JSON parsing algorithms we commonly use are based on scalar state machine parsers. Scalar parsers read the input string byte by byte, parsing it through state transitions within the state machine. For example: When encountering a quotation mark ("), it indicates the start of a string. When encountering a colon (:), it indicates that a value is expected next. Below is a simplified pseudo-code representation of how a scalar parser works ...
Kotlin Coroutine Internals: Suspension, Continuation, CPS EN
This post explains how coroutines work, referencing the design proposal Kotlin Proposals - Coroutines. Coroutine The proposal describes a coroutine in one sentence as an instance of suspendable computation. The essential trait of a coroutine is its ability to suspend. So what exactly does “suspendable” mean? Suspension According to the proposal, suspendable means a coroutine can pause execution on the current thread, yield the thread so another coroutine can run, and later resume—possibly on a different thread. ...